CD38 Inhibitor Program
CD38 Inhibitor Program — Reversing Immunosuppression by Restoring T Cell Fitness in the Tumor Microenvironment
We are developing small molecule inhibitors of another NAD+-utilizing enzyme, CD38, a stress-induced protein linked to immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment allowing cancers to grow. CD38 is overexpressed in a number of cancers, including lung and prostate cancers. The catalytic activity of CD38 is important to its immunosuppressive activity. Although two anti-CD38 antibodies, daratumumab and isatuximab-irfc, have been approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma, these anti-CD38 antibodies are unable to inhibit intracellular CD38, unlike our small molecule inhibitors, which we believe can. CD38 expression can also increase in response to treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors, which may lead to resistance against these therapies. Inhibition of CD38 may overcome this resistance, and we have observed in mouse models potential benefits of combining CD38 inhibitors with immune checkpoint inhibitors. We are not aware of any small molecule drugs or small molecule drug development programs that target CD38.
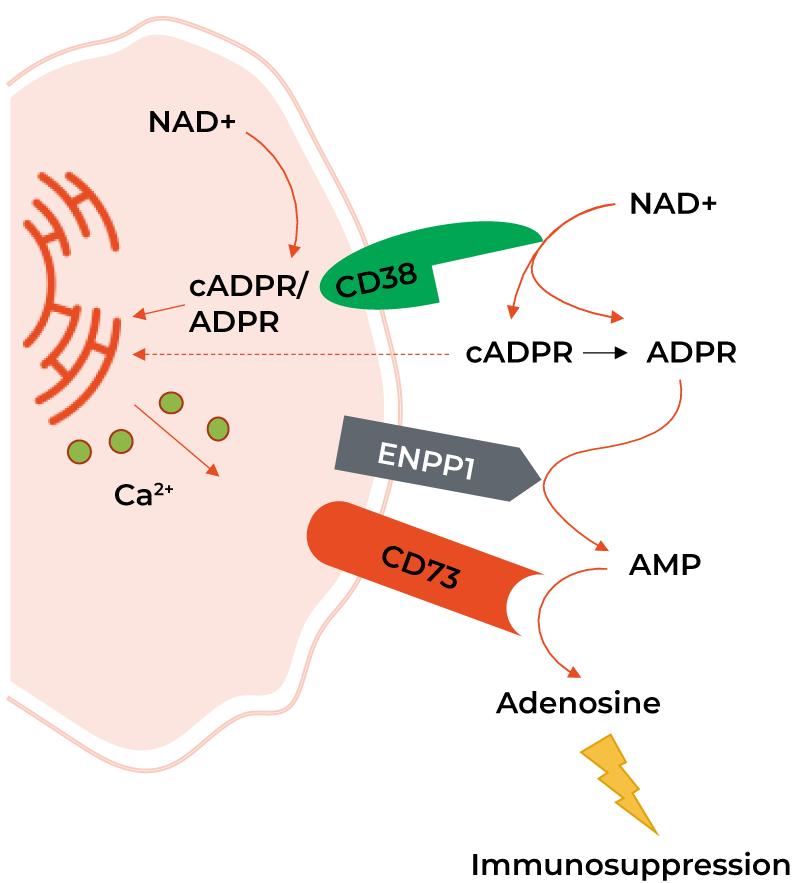
CD38 is overexpressed in a number of cancers, including lung and prostate cancers. The catalytic activity of CD38 is important to its immunosuppressive activity.